 |
| Home Intro Technical History Crew Models Gallery Kriegsmarine Archives More Forum Español UPDATES |
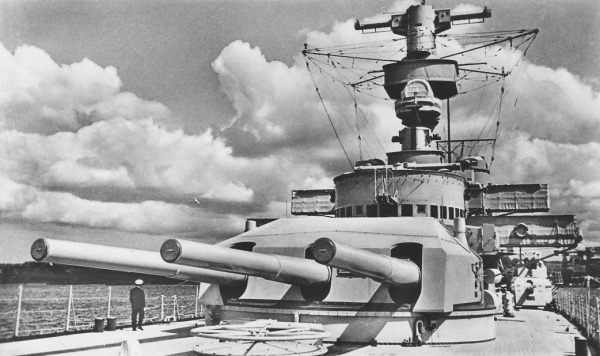
 The Deutschland was the first ship of a new type known as Panzerschiff (armoured ship), referred to as "pocket battleship" by the British.
The Deutschland conducted several non-intervention patrols off the coast of Spain during the Civil War (1936-1939).
In 1937, while anchored off the Balearic island of Ibiza, the Deutschland was bombed by a Loyalist Spanish plane.
This prompted the bombing of Spanish Republican positions off Almeria, by her sister ship Scheer in retaliation.
In the days previous to the outbreak of the war in Europe, the Deutschland departed for the Atlantic to attack British merchant shipping, but was soon recalled on Hitler's orders and renamed Lützow for prestige reasons.
An unlucky ship, the Lützow was torpedoed in April 1940, and again in June 1941 when trying to reach Norway.
That kept the ship in the shipyard for most of the time during the first couple of years of the war.
In 1942, the Lützow was sent to Norway, but her only real chance to engage the enemy at sea on New Year's Eve proved a failure.
On her return to Germany, the Lützow was used as a training ship in the Baltic and for the shore bombardment of Soviet forces.
In April 1945, while anchored in Swinemünde, the ship was bombed and later scuttled by the crew.
The Deutschland was the first ship of a new type known as Panzerschiff (armoured ship), referred to as "pocket battleship" by the British.
The Deutschland conducted several non-intervention patrols off the coast of Spain during the Civil War (1936-1939).
In 1937, while anchored off the Balearic island of Ibiza, the Deutschland was bombed by a Loyalist Spanish plane.
This prompted the bombing of Spanish Republican positions off Almeria, by her sister ship Scheer in retaliation.
In the days previous to the outbreak of the war in Europe, the Deutschland departed for the Atlantic to attack British merchant shipping, but was soon recalled on Hitler's orders and renamed Lützow for prestige reasons.
An unlucky ship, the Lützow was torpedoed in April 1940, and again in June 1941 when trying to reach Norway.
That kept the ship in the shipyard for most of the time during the first couple of years of the war.
In 1942, the Lützow was sent to Norway, but her only real chance to engage the enemy at sea on New Year's Eve proved a failure.
On her return to Germany, the Lützow was used as a training ship in the Baltic and for the shore bombardment of Soviet forces.
In April 1945, while anchored in Swinemünde, the ship was bombed and later scuttled by the crew.
09 February 1929: Lay down on Slipway 2 at Deutsche Werke, Kiel. Construction number 219.
19 May 1931: Launched. Christened by President von Hindenburg.
27 February 1933: Passes through the Kiel Canal en route to Wilhelmshaven.
01 April 1933: Commissioned under Captain Hermann von Fischel.
20 May - 01 June 1933: Deutschland departs Wilhelmshaven for Kiel via the Skagerrak, and from there goes into the Norwegian Sea and the faroe islands, returning to Wilhelmshaven on 1 June.
31 July 1933: Departs Kiel for the Baltic Sea.
August-September 1933: Conducts sea trials in the Baltic. On 23 August 1933, the ship performs a series of measured mile runs off Neukrug in the Bay of Danzig achieving a speed of 28 knots at 48,390 hp.
10-14 April 1934: Deutschland visits Hardangerfjord and Sognefjord in Norway with Adolf Hitler aboard, together with the Minister of Defence Generaloberst Werner von Blomberg, and the Commanders-in-Chief of the Army and Navy, General Werner von Fritsch and Admiral Erich Raeder.
28 May - 01 June 1934: Visit to Hamburg coinciding with the anniversary of the battle of Jutland on 31 May.
09-23 June 1934: North Atlantic cruise with light cruiser Köln.
August 1934: Visit to Leith, Scotland.
06-20 October 1934: Visit to Edinburgh with Konteradmiral Rolf Carls aboard.
13 December 1934 - 21 February 1935: At Wilhelmshaven.
14 March - 19 April 1935: Atlantic cruise. The ship crosses the Equator for the first time on 27 March, and later calls at Port of Spain, Trinidad (03-06 Apr.) and San Nicolaas, Aruba (08 Apr.).
20 August 1935: Passes through the Kiel Canal en route to Kiel for fleet gunnery exercises.
26-27 August 1935: The ship is visited by Adolf Hitler accompanied by the Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces Generaloberst Werner von Blomberg, General der Flieger Hermann Göring, and the Commander-in-Chief of the Navy Admiral Erich Raeder.
28 August 1935: Made fast to Buoy A 7 (Kiel).
30 August 1935: Passes through the Kiel Canal en route to Brunsbüttel.
31 August 1935: Arrives in Wilhelmshaven.
19 October - 09 November 1935: Training cruise in the Atlantic with her sister ship Admiral Scheer. Anchored in Funchal, Madeira on 25-28 October. Arrives in Wilhelmshaven on the 9th, via the English Channel.
29 May 1936: Participates in the fleet parade for the inauguration of the naval memorial at Laboe, near Kiel.
06-19 June 1936: Together with the Admiral Scheer cruise through the English Channel, Irish Sea, Orkney-Shetland Channel, Skagen, returning to Kiel.
24 July - 31 August 1936: Departs Wilhelmshaven together with the Scheer for operations in Spanish waters.
01 October - 21 November 1936: Operations in Spanish waters.
31 January - 24 March 1937: Operations in Spanish waters.
10 May 1937: Departs for the Mediterranean.
29 May 1937: Attacked by Spanish loyalist planes while anchored in Ibiza. Deutschland is hit by two 50kg bombs. The damage is slight but 37 men die.
30-31 May 1937: Calls at Gibraltar.
16 June 1937: Arrives in Wilhelmshaven. State funeral.
05 October 1937 - 11 February 1938: Operations in Spanish and Italian waters with calls at: El Ferrol (11 Oct.), Cadiz (12-14 Oct.), Gibraltar (18-19 Oct.), Tangier (20-24 Oct.), Algeciras (25-26 Oct.), Ceuta (1 Nov.), Melilla (2 Nov.), Gaeta (5-8 Nov.), Algeciras (18-22 Nov.), Cadiz (23-25 Nov.), Gibraltar (25-27 Nov.), Tangier (3-5 Dec.), Cadiz (6-9 Dec.), Larache (11-12 Dec.) Cadiz (13-14 Dec.), Algeciras (16-17 Dec.), Naples (21-31 Dec.), Capri (5-7 Jan), Amalfi (7-10 Jan), Taormina (11-13 Jan.), Cadiz (26-28 Jan.), Lisbon (29 Jan-7 Feb.), El Ferrol (8 Feb.), English Channel (10 Feb.), Wilhelmshaven (11 Feb.).
24 Juy - 15 August 1938: Operations in Spanish waters including call at Algeciras (8 Aug.)
22 August 1938: Participates in the naval review following the launching of the heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen in Kiel.
20 September - 20 October 1938: Atlantic cruise fully equipped for war due to the Sudeten crisis.
06 January - 26 February 1939: Operations in Spanish waters. Itinerary: Wilhelmshaven (6 Jan.), Tenerife (11-13 Feb.), La Palma (17-19 Feb.), El Ferrol (23 Feb.), English Channel (25 Feb.), Wilhelmshaven (26 Feb.).
23 March 1939: Deutschland departs Swinemünde eastbound with Adolf Hitler aboard to be present in the annexation of Memel Territory.
01 April 1939: At Wilhelmshaven during the launching of the battleship Tirpitz.
17 April - 16 May 1939: Atlantic cruise with calls at Vigo (27 Apr.) and Malaga (1 May).
24 August 1939: Departs Wilhelmshaven bound for the north Atlantic as a precautionary measure in case war breaks out.
28 August 1939: Transits the Denmark Strait into the Atlantic.
03 September 1939: The United Kingdom and France declare war on Germany following the German invasion of Poland on 1 September.
26 September 1939: The Deutschland is ordered to leave her waiting area and commence hostilities against British merchant shipping.
05 October 1939: Sinks the Stonegate (5.044 GRT) 600 nautical miles east of Bermuda.
09 October 1939: Captures the American steamer City of Flint (4.963 GRT).
14 October 1939: Sinks the Norwegian steamer Lorentz W Hansen (1.918 GRT) 400 nautical miles east of Terranova.
07-08 November 1939: Transits the Denmark Strait on her way back to Germany.
15 November 1939: After passing through the Skagerrak, the Kattegat, and the Great Belt, the Deutschland arrives in Gotenhafen and is renamed Lützow.
24-25 November 1939: Lützow together with the light cruisers Leipzig, Köln, and four destroyers, sortie into the Skagerrak to divert enemy attention from the battleships Scharnrhost and Gneisenau.
26 November 1939: Arrives in Wilhelmshaven.
28 November 1939: Departs Wilhelmshaven eastbound for the Baltic via the Kiel Canal.
December 1939 - January 1940: Dockyard period. Repairs to hull and engines at Danzig.
01 February 1940: Available for operations in Gotenhafen. Ship reclassified as heavy cruiser.
12-13 March 1940: Transferred to Swinemünde.
14 March 1940: At Swinemünde with Emden
18-19 March 1940: Transferred from Swinemünde to Kiel with Emden and oiler Nordmark.
06 April 1940: Operation Weserübung. Lützow is assigned to Group 5, under the command of Konteradmiral Oskar Kummetz destined for Oslo. The ship embarks 400 soldiers at Wilhelmshaven, and later passes through the Kiel Canal en route to Kiel.
07 April 1940: Shortly after noon, Lützow arrives in Kiel where she is later joined by the heavy cruiser Blücher (flagship), the light cruiser Emden, and the torpedo boats Kondor, Albatros, and Möwe, from Swinemünde. Shortly afterwards, motor minesweepers R18 and R19 join the squadron forming Battlegroup 5. In the evening the group anchors in the Kiel Fjord.
08 April 1940: At 0300 hours, Battlegroup 5 weighs anchor northbound. During the night the German ships pass through the Great Belt and then reach the Kattegat.
09 April 1940: Shortly after midnight, Battlegroup 5 enters the Oslo Fjord. The Blücher leads the group, followed by the Lützow, Emden and the torpedo boats. At 0518 hours, as the Germans near the Drøbak narrows, the Blücher comes under fire from the Norwegian shore batteries (3 x 28cm guns) at Oskarsborg fortress. The cruiser is hit at short range on the port side. Blücher returns fire ineffectively. At 0530 hours, the ship is hit by two torpedoes on the port side. The Lützow is also hit by gunfire. One 15cm shell striking the central barrel of the forward turret that is temporarily put out of action. Unable to shoot back effectively and force the Drøbak narrows, the Lützow moves back and later lands her troops at Sonsbukten. Meanwhile, the Blücher finally capsizes and sinks at 0727 hours off Askholmen island with heavy loss of life.
10 April 1940: Lützow and Emden put in to Oslo. In the evening, the heavy cruiser departs Oslo for Kiel.
11 April 1940: At about 0200 hours, during the return voyage back to Germany, the Lützow is torpedoed by the British submarine Spearfish (Commander John H. Forbes) at about 12 nautical miles northeast of Skagen (quadrant AO 4462). The ship is hit by a 21-inch MK VIII torpedo and the stern breaks off damaging the rudder and propellers. Unable to steer, the ship is taken in tow through the Kattegat to Kiel. Casualties: 15 dead.
13 April 1940: Arrives in Kiel at 2022 hours.
May-December 1940: Repairs at Deutsche Werke, Kiel.
Night of 8-9 July 1940: During an air raid by British aircraft on Kiel, the Lützow, lying in the yard, is hit by a bomb that fails to detonate.
31 March 1941: Captain Leo Kreisch assumes command of the ship at Scheerhafen, Kiel.
08 April 1941: A Japanese delegation from Japan's Naval Mission in Germany visits the ship.
09 April 1941: Departs Kiel bound for Gotenhafen to conduct sea trials in the Baltic.
10 April 1941: Arrives in Gotenhafen and anchors in the roadstead at 2105 hours.
12-17 April 1941: Moored at Becken IV, Gotenhafen.
18 April 1941: Performs measured mile runs off Neukrug.
19-23 April 1941: Moored at Becken IV, Gotenhafen.
02 May 1941: Leaves Gotenhafen westbound for Swinemünde.
03-16 May 1941: At Swinemünde.
17 May 1941: Anchors in the Bay of Danzig.
10 June 1941: Operation Sommerreise. Transfer from Gotenhafen to Trondheim, Norway. In the afternoon, Lützow departs Gotenhafen and sails west to Kiel.
11 June 1941: Departs Kiel in the evening escorted by destroyers Hans Lody, Friedrich Eckoldt, Karl Galster, Z23 and Z24.
13 June 1941: At about 0220 hours, the Lützow is hit amidships on the port side (Section VII) by a 18 inch MK XII torpedo dropped by a British Beaufort aircraft (Flight Sergeant Ray Loveitt), 25 nautical miles west of Egersund (quadrant AN 3186).
14 June 1941: The damaged Lützow arrives in Kiel.
June-December 1941: Under repair at Deutsche Werke, Kiel (Dock VI).
05 January 1942: Captain Rudolf Stange assumes command of the ship in Kiel.
20 January: Arrives in Gotenhafen.
23 January - 09 April: At Swinemünde.
10 April - 21 April: At Danziger Werft, Danzig.
21 April 1942: Admiral Raeder inspects the ship at Danziger Werft.
May 1942: At Swinemünde.
16 May 1942: Operation Walzertraum. Transfer of Lützow from Germany to Norway. Departs Swinemünde escorted by destroyers Richard Beitzen, Z29, and escort boat F1. In the evening, destroyers Hans Lody and Z27 join the group off Kiel.
17 May 1942: After passing through the Great Belt, the Kattegat, and the Skagerrak, Lützow anchors off Kvarenes east of Kristiansand.
18-20 May 1942: At 2345 hours on the 18th, Lützow is transferred from Kristiansand to Trondheim.
20-25 May 1942: Anchored at Lofjord east of Trondheim.
25 May 1942: Operation Lohengrin. Transfer of Lützow from Trondheim to Narvik. Lützow and oiler Nordmark arrive at Bogen Bay with destroyers Richard Beitzen, Z27, and Z29.
03 June 1942: In his capacity as Admiral Commanding Cruisers (BdK), Vizeadmiral Oskar Kummetz takes over command of the Narvik task force, and makes Lützow his flagship. The following units are now stationed in Narvik: Lützow, Admiral Scheer, and six destroyers.

The heavy cruiser Lützow anchored in Bogen Bay near Narvik in June 1942.
02 July 1942: Operation Rösselsprung. At midnight, the heavy cruisers Lützow and Admiral Scheer leave Narvik under the command of Vizeadmiral Kummetz, together with destroyers Z24, Z27, Z28, Z29, and Z30. They are to join in Altafjord with the battle group from Trondheim under the command of Admiral Otto Schniewind and comprised of the battleship Tirpitz, the heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper, the destroyers Friedrich Ihn, Hans Lody, Karl Galster, Theodor Riedel, and the torpedo boats T7 and T15. Once in Altafjord their mission is to attack the convoy PQ17 with 36 merchantmen.
03 July 1942: At 0245 hours, the Lützow runs aground at the entrance of the Tjeldsund due to fog and returns to Narvik, eliminating her from the operation. The rest of the German battle group gathers in Altafjord, and although in the end the enemy is not engaged, its mere presence forces PQ17 to scatter resulting in the loss of 22 merchantmen at the hands of the Luftwaffe and U-boats.
09 July 1942: Lützow, destroyers Z24 and Friedrich Ihn, are transferred from Narvik to Trondheim.
10 July - 09 August 1942: Anchored at Lofjord, Trondheim.
10 August 1942: Operation Eiche. Lützow is transferred from Trondheim to the Baltic escorted by torpedo boats T6, T15, T9, T12, and escort boat F1.
12 August 1942: Lützow arrives in Swinemünde.
August-October 1942: Undergoes structural repairs at Deutsche Werke, Kiel.
November 1942: Runs trials in the Baltic Sea.
08 December 1942: Operation Prometheus. The Lützow departs Gotenhafen bound for Norway, together with destroyers Karl Galster, Theodor Riedel, and Z31.
12 December 1942: Lützow arrives at Bogen Bay on the afternoon with destroyers Theodor Riedel and Z31 (Galster having been detached to Trondheim).
16 December 1942: Operation Rudelsburg. Departs Bogen Bay northbound for Altafjord with Theodor Riedel and Z31.
18 December 1942: Arrives at Altafjord and anchors in Kåfjord.
30 December 1942: Operation Regenbogen. The heavy cruisers Lützow and Admiral Hipper (flagship), together with destroyers Friederich Eckoldt, Richard Beitzen, Theodor Riedel, Z29, Z30, and Z31, all under the command of Vizeadmiral Oskar Kummetz, depart Altafjord to intercept convoy JW51B that has been previously reported by U-354 (Kapitänleutnant Karl-Heinz Herbschleb).
01 January 1943: The German squadron arrives at Altafjord.
10-11 March 1943: Operation Thüringen. Lützow is transferred from Altafjord to Bogen Bay together with destroyers Theodor Riedel, Z31 and minelayer Brummer.
11-23 March 1943: Anchored at Bogen Bay near Narvik.
23-24 March 1943: Operation Silesia. Lützow together with Tirpitz, Scharnhorst, and six destroyers are transferred to Altafjord.
April-July 1943: Runs trials in Altafjord.
23 September 1943: Operation Hansa-Hermelin. Transfer to Germany for a dockyard refit. In the evening, the Lützow departs Altafjord southbound together with the destroyers of 5th Flotilla Paul Jacobi, Erich Steinbrinck, Friedrich Ihn, and Z27.
25 September 1943: In the afternoon, Lützow and destroyers anchor at Skjomen Fjord near Narvik.
27 September 1943: Lützow group sighted by British reconnaissance planes south of Stadlandet. Off Kristiansand destroyer Friedrich Ihn is detached.
29 September 1943: Lützow group off Ven Island at 0800 hours. At 2000, when off Rügen Island, destroyers Paul Jacobi and Erich Steinbrinck are detached to Kiel. Lützow continues alone into the eastern Baltic.
30 September 1943: Lützow anchors in Danzig Bay at 1000 hours.
01 October 1943: Enters Gotenhafen.
January-March 1944: Rapairs at Libau.
24 June 1944: Departs Gotenhafen at 0700 hours for operations in the Gulf of Finland. At 1800, rendezvous at sea (quadrant AO 5998) with torpedo boats of the 2nd Flotilla, T12, T3 and T4 from Libau.
08 July 1944: Arrives in Gotenhafen.
09 August 1944: Docks in Gotenhafen.
10-15 October 1944: Lützow, together with Prinz Eugen (flying the flag of Vizeadmiral August Thiele), three destroyers, and four torpedo boats carry out support operations off the coast of Memel against the advancing Soviet armies.
23 November 1944: Sent to the Sworbe peninsula on the island of Ösel to provide shore bombardment against Soviet positions, but by the time it arrives the Germans have already been evacuated.
16 April 1945: Attacked by 18 Lancaster bombers in Swinemünde. The ship is heavily damaged by the near-miss of a Tallboy bomb and sinks in shallow water, but the hull comes to rest on an even keel with all superstructure above water.
28 April 1945: Turret "A" is put back in service and still fires over 300 x 28cm shells on the Soviets.
04 May 1945: After expending all ammunition the ship is scuttled in Swinemünde.
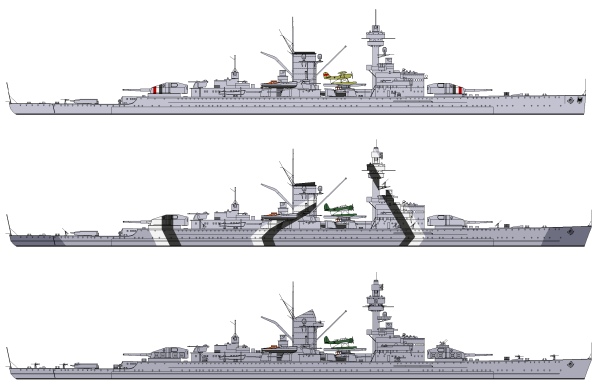
The Deutschland as she looked during the Spanish Civil War (top), in 1941 (center), and in 1944 (botton).
01 April 1933 - 03 September 1935: Kapitän zur See Hermann von Fischel.
30 September 1935 - 03 September 1937: Kapitän zur See Paul Fanger.
05 October 1937 - 16 November 1939: Kapitän zur See Paul Wennecker.
16 November 1939 - April 1940: Kapitän zur See August Thiele.
31 March 1941 - July 1941: Kapitän zur See Leo Kreisch.
05 January 1942 - 10 November 1943: Kapitän zur See Rudolf Stange.
January 1944 - April 1945: Kapitän zur See Bod-Heinrich Knoke.
April - May 1945: Fregattenkapitän Ernst Lange.
Displacement: standard 11,900 mt, full load 14,290 mt.
Dimensions: Waterline length 181.7 m, overall length 186 m, beam 20.64 m, maximum draft 7.2 m, depth 12.2 m.
Armour: main belt 80 mm (13º inclined), turrets 70-160 mm, armour deck 20-40 mm, conning tower 150 mm, torpedo bulkhead 40 mm.
Armament:
• 6 x 28cm SK C/28 guns in two triple turrets.
• 8 x 15cm SK C/28 guns in single turrets.
• 6 x 8.8cm SK C/31 guns in three double mounts (later replaced with 6 x 10.5cm SK C/33 guns).
• 8 x 3.7cm SK C/30 guns in four double mounts.
• 10 x 2cm MG C/30 guns in single mounts.
• 8 x 53.3cm torpedo tubes in two quadruple mounts.
Fire control:
• 4 x 10.5-m base rangefinders.
• 1 x 7-m base rangefinder.
Radar equipment:
• In 1940: 1 x FuMO 22.
• In 1941: 2 x FuMO 26.
Seaplanes: 1 x Heinkel He-60 (replaced in 1939 with 1-2 x Arado ar 196).
Propulsion plant: 8 x MAN diesel engines, two shafts, 54,000 hp. One rudder.
Speed: 26 knots (designed), 28 knots (at 48,390 hp on trials).
Endurance: 17,400 nm at 13 knots, 11,600 nm at 19 knots, 7,900 nm at 22 knots.
Fuel capacity: 2,750 mt.
Crew: 1,150 (wartime approx.).

| Home Guestbook Quiz Glossary Help us Weights & Measures Video Credits Links Contact |
